A good understanding of web development is required to follow this article.
If your embedded YouTube videos have suddenly stopped playing on your website, you are not alone. Instead of loading the player, they may now display the message "Error 153: Video player configuration error."
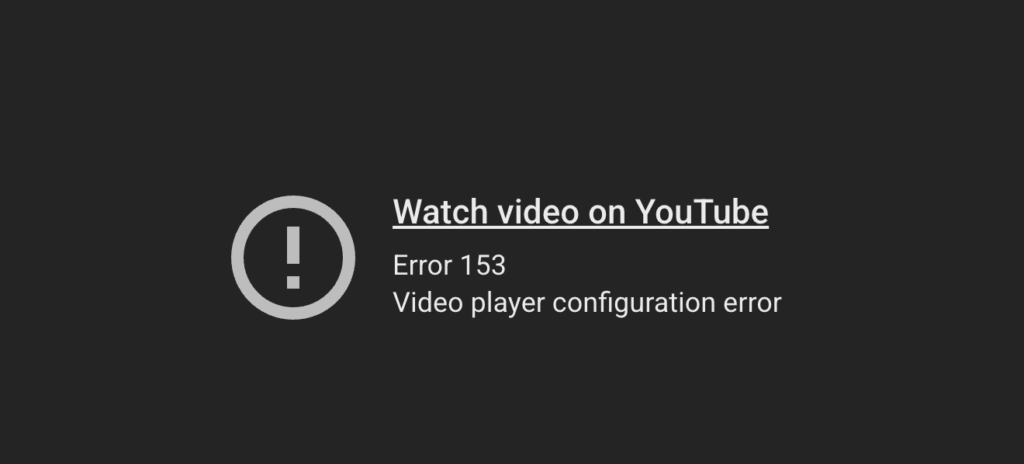
If you right-click on the error screen and select "Copy debug info," you’ll find the following text in the copied data:
"debug_error": "{\"errorCode\":\"embedder.identity.missing.referrer\"
The cause of this issue is the referrer policy. YouTube expects a valid referrer. When the embedded YouTube URL loads on a page where the referrer policy is set to "no-referrer," it triggers Error 153. This was likely tolerated previously, but Google appears to have tightened the policy recently, which has led to the problem.
To confirm the problem, open your webpage in Google Chrome, open Developer Tools, switch to the Network tab, find the YouTube embed link, click it, and check the Referrer Policy value in the Headers tab on the right.
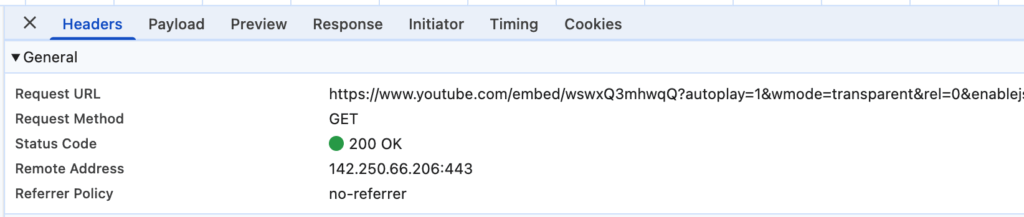
To fix the problem, you will need to change the referrer policy of the YouTube embed URL from "no-referrer" to another value, for example, "strict-origin-when-cross-origin", which is a common value.
The "no-referrer" policy may be inherited from your webpage. Open your webpage in Google Chrome, open Developer Tools, switch to the Network tab, find the page URL, click it, and then check the Referrer Policy in the Headers tab on the right.
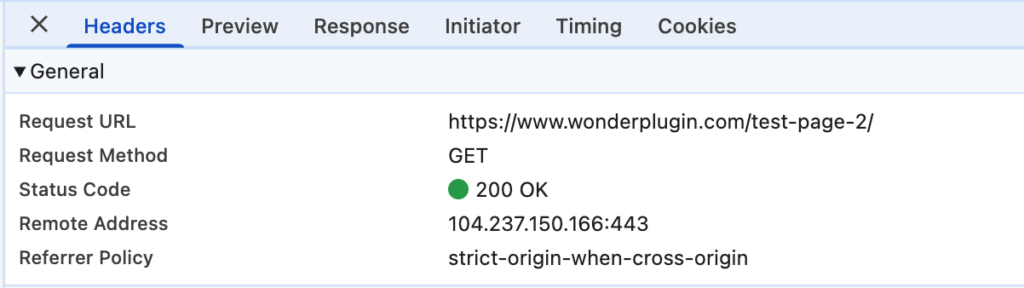
If the value is "no-referrer," it may have been configured by your web hosting provider, set in the .htaccess file in your WordPress directory, or enforced by a WordPress security plugin.
If the page already has the correct referrer policy (for example, "strict-origin-when-cross-origin"), check if there is a referrerpolicy value configured in the YouTube embed code. An iframe can include a referrerpolicy attribute, which influences the policy for that frame.
The policy of the YouTube embed URL could also be affected by a meta tag on the page. For example, the following code forces all links on the page to use the “no-referrer” policy:
<meta name="referrer" content="no-referrer">
<meta name="referrer" content="never">
This meta tag may have been added by your WordPress theme or dynamically inserted by a third-party plugin. In Google Developer Tools, switch to the Elements tab, search for the word "meta", and check whether such a tag exists.
